
I left work Friday afternoon in a pouring rain. Nothing unusual in the grand scheme of things. It is late March and Spring had sprung this week, which usually brings rain. An entire week of rain, in fact. I had hoped, against all evidence to the contrary, that the rain would let up earlier in the day on Friday. I resigned myself to retrieving my vanpool riders and slogging through rain drenched traffic for the next hour. I wanted to participate in my astronomy club‘s Messier Marathon, but just didn’t think the effort would equal the returns. I would have to pack up all of my astronomical observing equipment (telescope, tripod, eyepieces, control device, cables, portable battery, sky charts, observing aids, red flashlight, chair, some kind of table, etc) and then drive over an hour to the dark sky site way south near Butler, Missouri. Early indications from other club members reported the dark sky site field was very wet and since I don’t own a four-wheel drive truck or SUV, I decided to stay in Lansing.
I had permission from my city council representative to contact the Chief of Police to make arrangements to use one of the city parks after dark. I hesitated to bother the police. That is a huge hassle to overcome, for me anyway. And I still needed to re-train my telescope’s Alt/Az drives before packing them up, since that process requires daylight and a terrestrial object to focus upon. Clouds still scudded across the sky while I set the telescope up outside on the lower back patio. I trained the drives for five or ten minutes and then powered down the telescope until later in the evening.

After watching a couple of episodes of Jeopardy and squeezing in my exercise routine (and making my legs wobbly and rubbery by trying a longer version of one of the higher intensity activities), I slipped back outside to see how many stars were visible at just a few minutes past eight o’clock. I spied the small sliver of a new crescent moon hovering just over my neighbor’s roof so I grabbed my camera (already on it’s tripod) and took a few photos (two of which I am including in this post). I even got Terry outside long enough to witness the new moon and point out how much higher Venus has gotten over Jupiter in a week since the last time I photographed the pair of them.
By the time I finished snapping a few photographs, I had enough bright stars to attempt an alignment of the telescope with my newly retrained drives. The Autostar easy alignment selected Sirius in Canis Major as the first star in the alignment process. After I found and centered the Dog Star, the next stop on the alignment workflow became Capella in the constellation Auriga, another easily spotted star in the evening sky. The Autostar reported a successful alignment so now for the first real test of the retrained drives. I instructed the device to find Jupiter. Surprise! The telescope found Jupiter on the first try! I did have to recenter Jupiter and it’s four glorious moons in the eyepiece, but I did not have to use either of my finder scopes. I inserted a 2x barlowe and a 26mm eyepiece and could clearly see the cloud striations on Jupiter. I could even see a hint of color. I again pulled Terry out to the telescope to take a look at the gas giant and its beautiful alignment of moons.
Next stop on my pre-Messier tour became Venus. Again the Autostar found our sister planet successfully. I only had to re-center the very bright planet in my eyepiece. I should have put a filter on the eyepiece, because even at only half-full, Venus almost hurt my eyes to look at. I felt confident enough in the telescopes alignment and the retrained drives to begin my mini-Messier Marathon.
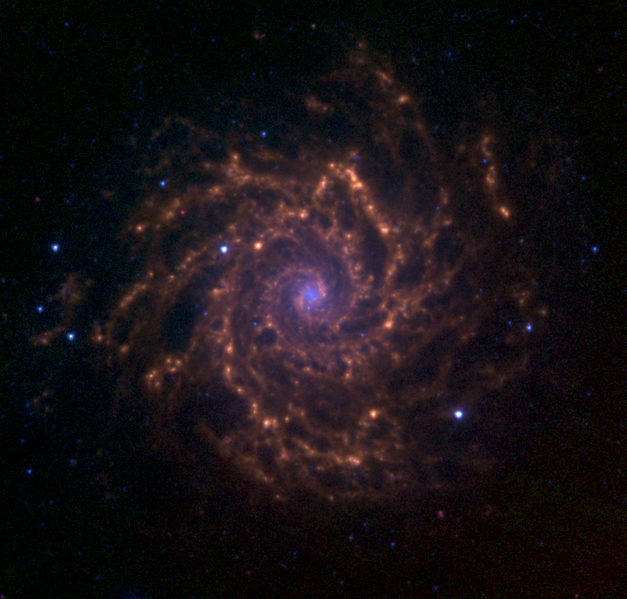

My Messier Marathon Observer’s Form lists the objects in a ‘best viewed in this order’ arrangement. I knew I would not be able to observe the first two items on the list, due to the nature of my site. My house rests in a valley, behind a large hill to my west. In addition, I have several tall trees in my backyard, as do my neighbors to the west and north. Thanks to the highway just a couple of blocks to my west, I have ample ambiance (aka light pollution) and nearly all my neighbors must be afraid of the dark because they insist on illuminating nearly all exterior surfaces of their residences. Still, I told the Autostar to go find M77, a spiral galaxy also known as Cetus A. Unfortunately, the telescope came to rest pointing northwest, through at least three trees. I moved on to the next item, M74, another spiral galaxy in the constellation Pisces. But again, I saw only trees. A shame, really, as I would love to see that beautiful spiral galaxy (shown in photo above and to the left).
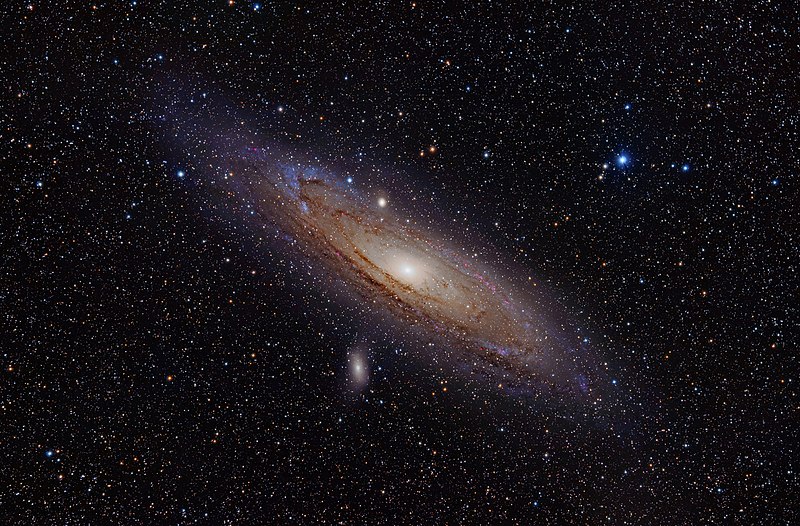

The next three stops on the observation list also happened to be galaxies, including the famous Andromeda galaxy, designated as M31 on the Messier list of objects. Since the telescope did not move appreciable away from the area of M77 and M74, I again couldn’t see the stars for the forest. Yet another galaxy I desperately want to observe, so to ease the pain of defeat, I’ll provide another image of that marvelous gem. The image above and to the right also includes M32, one of the other two galaxies I couldn’t observe.
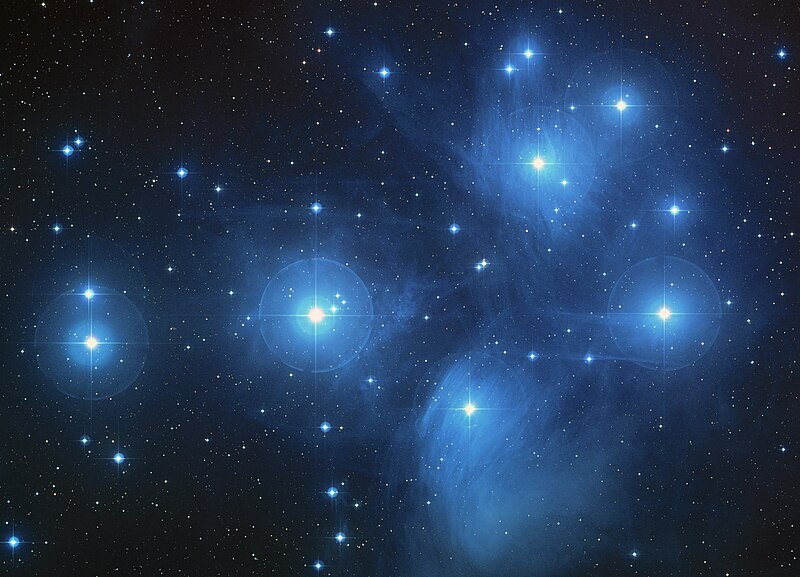

I began using my Sky & Telescope Pocket Sky Atlas to assist me in locating Messier objects that I could actually view in my limited sky scape. The Pocket Sky Atlas‘s last pages contains an index of Messier objects and the star chart they appear on. I skimmed through the list of the next few objects and determined that M45 could be seen with the naked eyes. The Pleiades is an open star cluster. I still told the telescope to go find it and spent a few minutes marveling at the cluster of bright stars peering back at me through the eyepiece. Finally, I got to check off one of the 110 objects on my Messier Marathon Observer’s Form, writing 8:42 p.m. in the blank provided.
The next two objects I found easily included M42 and M43, both found in Orion’s sword and more commonly known as the Great Orion Nebulae and De Marian’s Nebula (really part of the other one or an extension of it). I wrote 9:07 p.m. in the blanks on my form.

I spent the next thirty to forty minutes trying to track down several objects I should have been able to find since they were south or directly overhead. I could not find the Crab Nebula (M1) and began to suspect I had messed up the alignment on the telescope. I had nudged a tripod leg more than once, so I reverted the Autostar to star mode and went searching for Rigel, Betelgeuse, Sirius and Capella again to retune the alignment. After that, I was successful in viewing several star clusters, including M44 (aka the Beehive Cluster), M48 and M50 (between 9:45 and 9:51 p.m.).

I got even more excited when I spied M95 on the list just two below M44. This spiral galaxy gained fame this past week by spouting a supernova. My earlier research also showed that Mars was just a few degrees away from M95. So I took a few minutes to realign the telescope and enjoy the ruddy beauty of the fourth planet in our solar system. Then I went on the hunt for M95. I spent many frustrating minutes attempting to find the elusive spiral galaxy but to no avail. The skies above Lansing are just not dark enough for my small telescope. It can’t gather enough light and my aging eyes can’t ever seem to get acclimated to the annoying and obscuring local ground illumination to spot such a faint (9.7 in magnitude) object. By a quarter after ten, I decided enough was enough.
And, for some unknown reason, the telescope had twice decided to go off on a tangent, causing the altitude drive to run off for no reason and would not stop when I entered commands into the Autostar. Hmmm. There must be a bug in the latest firmware I downloaded last week. I should probably hook the laptop up to it today and see if a ‘fix’ has been made available from Meade.
I enjoyed my mini-marathon of Messier objects and learned quite a bit about my abilities and the capabilities of my amateur astronomy equipment. Tonight I will attend the monthly meeting of the Astronomical Society of Kansas City and tomorrow I will probably head south to Powell Observatory for a training session on the club’s large telescope. By Monday, I should have purged my system of all astronomical cravings, at least until the next new moon.



 We observed
We observed